How Hearing Tests Can Detect Early Signs of Health Issues
Most people schedule hearing tests when they’re having trouble
Now offering the only FDA approved Tinnitus Treatment Device. LEARN MORE →

Most people schedule hearing tests when they’re having trouble

Often, changes in our hearing happen so slowly that we might not notice
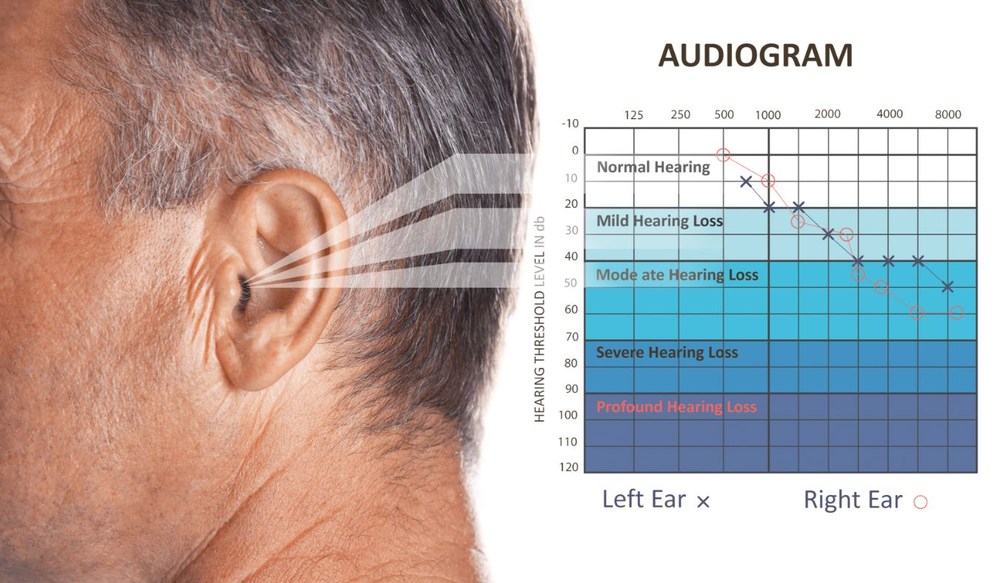
Getting to a hearing appointment isn’t always easy. Whether you live